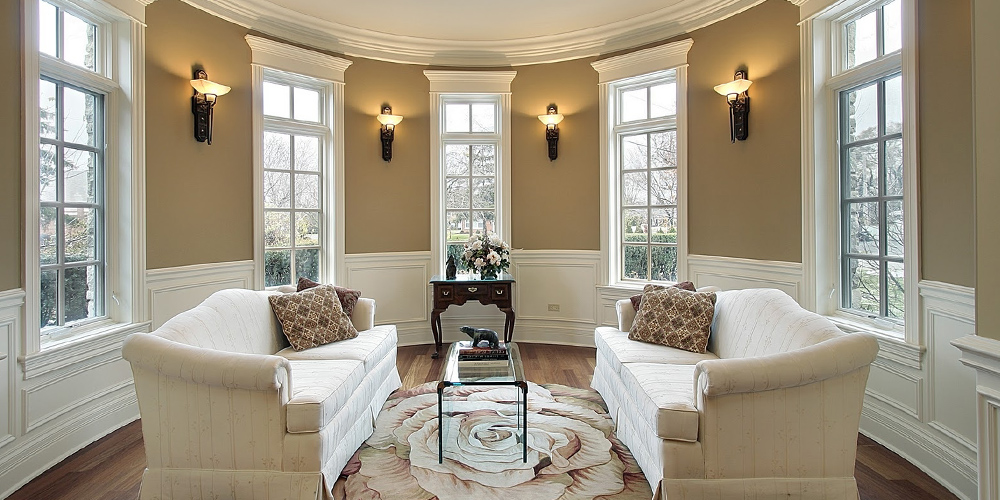



Wall lighting includes wall-mounted fixtures for use in indoor and outdoor settings. These types of lights provide general, ambient, or task lighting, and are popular for use in hallways, bathrooms, exterior entries, or to highlight wall features such as paintings or mirrors. With a variety of styles, types, and applications, wall lighting is a staple in lighting design, and can add both function and style to any space. Wall lights should be used in conjunction with additional general, task, and ambient light sources.
Wall lights are diverse in style and type. The most common option in wall lighting design is sconces. Other types of wall lights include track lights, picture lights, and vanity lights. Wall lighting fixtures can be crafted from almost any fixture materials, from bronze to glass to fabric. Outdoor wall lights will be crafted from weather-resistant metals, glass, or marine-grade plastic. Common components of wall fixtures include:
Wall lights use incandescent, LED, and fluorescent bulbs. Since these types of lights generally include stylized shades, the appearance of the bulb is generally not a stylistic consideration. Each bulb types carries unique advantages and disadvantages.
Wall lights can be powered in a variety of ways, depending on where they are positioned, their size, and their application. Most outdoor wall lights will run on a low voltage (12 volts) power system, though these lights can also be high voltage or solar powered. Low voltage lighting systems in indoor applications allow for a wider variety of bulb types, meaning small sconces may be low voltage to accommodate small bulb sizes. Other, large sconces will be high voltage, and very small task lights, such as wall mounted reading lights, may run on battery power. Each power system has unique benefits and deterrents.
Note: Always consult a professional lighting electrication before purchasing or installing any lighting system. This guide is not intended to take the place of a professional's best opinion or serve as a technical safety manual.
Low voltage lighting systems are defined at 10V, 12V or 24V. Low voltage fixtures are a modern option, and were not previously available. Low voltage systems include low voltage fixtures, a transformer or power pack, and a low voltage electrical cable.
High voltage lights, or line voltage lights, are defined as 120V. Line voltage systems are the most popular option in indoor lighting applications.

The most common type of wall lighting is wall sconces. When picturing an indoor wall sconce, many people imagine an ornate, highly decorative wall-mounted fixture. However, modern wall sconces include a wide variety of styles and sizes, with many sleek, contemporary options available. Wall sconces consist of a backplate, extended arm, and light bulb hidden by a shade. Some sconces are adjustable, though this feature is more common to small swing arm or task wall lights. Wall sconces can have an on/off switch, but most are hard-wired and will operate on a line voltage system with other lights. A popular way to style wall sconces is in succession along a long hallway or stairwell. Wall sconces are found in any setting where added illumination or softened lighting is desired. Multi-light sconces include multiple bulbs and shades in their design, and are popular in spaces where more varied, dynamic light is desired, such as bathrooms or kitchens.

Outdoor wall sconces have an appearance similar to their indoor counterparts, but are crafted from weather-graded materials to withstand exposure to exterior elements. These types of lights include a caged housing design (as opposed to an open shade) to prevent water or snow from accumulating inside the light. Other outdoor wall lighting includes lanterns, and track lights. These fixtures uplight or downlight the vertical surface they are fixed to. Similarly to other outdoor lights, exterior wall lights help to eliminate shadows and illuminate hazards along walkways, in stairways, or in other dark spaces. Wall lights are popularly used to highlight doorways or street address numbers on the front of a home. With both decorative and functional value, outdoor wall lights add instant curb appeal.

Generally crafted from metal, swing arm lighting includes a hinged, extendable arm. These lights are highly adaptable, and can feature multiple adjustable components. The light source can be moved closer to or further from the wall, and also rotated. These types of lights are most commonly seen in bedrooms, and used for reading or to complete other tasks from the comfort of a bed. Swing arm lights are an ideal option in bedrooms with no space for a nightstand. Many swing arm lights include a dimmer and on/off switch. These types of lights can be highly stylized and used in other areas of the home.

Bath and vanity lighting is designed to offer even, glare-free lighting. These types of lights generally include multiple bulbs to achieve even illumination. Bath and vanity wall lights are task lights, designed to provide adequate illumination for tasks such as styling hair, putting on makeup, or brushing teeth. A vanity light mounted above a bathroom mirror or two sconces flanking each side of a mirror will offer effective task lighting in a average sized bathroom, and act as an ambient counterpoint to general overhead lighting. Many bath and vanity lights include thick, glass shades to cut down on glare and diffuse the light source.
Good to Know: Use daylight temperature bulbs for bath or vanity task lighting to ensure the most accurate depiction of color while performing personal hygiene and grooming tasks.

Track lights include two or more individual fixtures in fixed positions along one continuous track apparatus. Wall lighting is most popular as a ceiling light, but can be styled along a vertical wall as well. In wall-mount applications, track lighting can effectively illuminate an entryway or highlight a decorative object such as a painting. Track lights may include straight or curved tracks and flexible spotlights. Wall track lighting may be mounted in a vertical or horizontal orientation.

Picture lighting is a general descriptor to refer to lights that illuminate mounted artwork. These types of wall lights vary greatly in style and design. Many include multiple bulbs for an even distribution of light. Picture lights include a backplate, arm, and lightsource which is angled towards the highlighted artwork. Picture lights are generally placed above the artwork to be highlighted and downlight the piece.
Contemporary fixtures feature sleek lines and straight-forward styling. Geometric shapes, clean finishes, and modern glass are trademark indicators of the contemporary look.
Transitional lights bridge the gap between traditional and contemporary styles, lifting elements from both new and timeless design for a unique aesthetic. These fixtures may include sleek lines with some decorative ornamentation, elegant curved frames, and light detailing.
Traditional fixtures draw upon time-honored motifs for their design. Traditional lights are highly ornamental, and may recall a vintage European aesthetic. Popular features in traditional design include frosted glass, curved frames, and antiqued bronze finishes.
Popular in country or quaint home design, rustic lighting integrates organic shapes, textures, and weathering for a warm, relaxed look with regained modern appeal.
Craftsman lighting design mimics craftsman home design. Straight, simple lines, sharp angles, and contemporary materials are indicators of the craftsman style. Craftsman lights incorporate artistic hand-made style elements, such as painted finishings and seeded glass.
Contemporary industrial style mimics turn-of-the-century factory design, for a gritty, urban look. These lights use patinaed metals, vintage bulbs, and reclaimed motifs to achieve their signature aesthetic.
Wall lighting fixtures vary greatly in terms of size. Task wall lights should be proportional to the object they are styled against. For example, outdoor wall sconces should be proportional to the front door or garage door they flank, vanity lights should be proportional to the accompanying mirror, and picture lights should be proportional to the painting or artwork piece they highlight.
Ideal wall lighting placement depends largely on the application of the light, the room size, and the proportional placement of the object being illuminated.



